Iterative Mindset
Finding happiness in a constantly changing job market
by Mae White
University Innovation Fellow, IE University
This article was published in Change Forward, an annual publication from our program that features work by Fellows and their Faculty Champions.
A year ago, I came to my mom half in tears feeling defeated. I complained to her that as I prepared to graduate, I didn’t even know if I liked visual design enough to keep doing it as a job. I believed happiness could only be achieved when I reached a certain professional level, and I wasn’t going to get there if I didn’t land the perfect job. In hindsight, my hopeless outlook stopped me from jumping on opportunities that were not an exact match for my career, but were available at least. It made me wonder if this attitude was preventable. Was there a way to feel more capable of tackling problems by changing our expectations?
This brings us to the essence of design thinking. There are various phases of iteration, trial and error, and starting over, that I’ve ignored when it comes to my career. In order to better utilize design methodology in our lives, we must view our own careers as a problem solving process. By embracing this iterative nature, we can shift our mindset to one that is not only resilient to, but expects constant change.
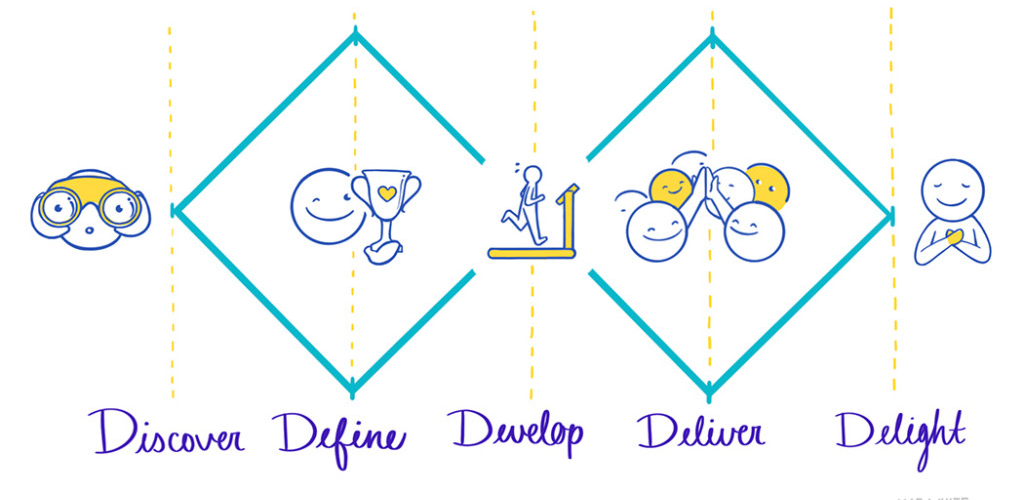
The double diamond method is a tactic to create a solution by gathering information from stakeholders, users, and their environment to arrive at an outcome best suited for them. The original idea hardly stays the same after going through this process. This can be applied to our career journeys as well.
The discovery phase is all about finding out which problems we care to solve. At this stage, we need to decide which values we want to let dictate our lives; is it money? Is it a passion? Can we fuse the two? What does society need right now that I can provide? We may find the focus shift away from ourselves and instead the problems we find most urgent. As we learn more about the world around us, the “how might we” questions start popping up. Can we join companies that are asking the same questions?
The second step is narrowing down these experiences to a niche that works best for you, and is provided by a greater need from the community. Though it’s no easy feat, define which mission you want to dedicate ample time to (it doesn’t have to be just one! It may also change later). Finding the answer to this question can give us more confidence to start the “prototyping” phase.
Rapid prototyping is where we try new jobs/projects constantly and when they don’t work out, we should ask ourselves “Why?”. What did our superiors tell us? What mistakes can we avoid making in the future? Maybe there are new things we didn’t know we wanted to pursue further! In dead end situations, pivoting is definitely an option.
Finally, when we find that our efforts are slowly making a dent in the problems we try to solve, it means we’ve arrived at our solution. This doesn’t mean to stop! Maybe we start something new, or inspire others who want to create the same changes you have to work alongside you.
The main takeaway is that we will feel defeated if we create a plan or idea of how our careers ought to be. Design thinking is all about being flexible and willing to pivot when an opportunity presents itself or our environment changes. Happiness can be attained throughout our design process; it’s not waiting for us at the end. Deciding to have an optimistic outlook on our circumstances, knowing that the road ahead will not be a smooth one, can make all the difference in motivating ourselves to move on to the next step. So, where will your design journey take you?













Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!